Thermal Treatment of Waste: An Efficient, Environmentally Sound Solution for Modern Cities
Waste to Energy (WtE), also known as Energy from Waste (EfW) is the state-of-the art approach to the treatment of municipal solid waste. In addition to the energy recovery component that gives the process its name, it also includes the effective incineration of the waste, a powerful waste gas purification system, and the recovery of valuable materials from the residual materials.
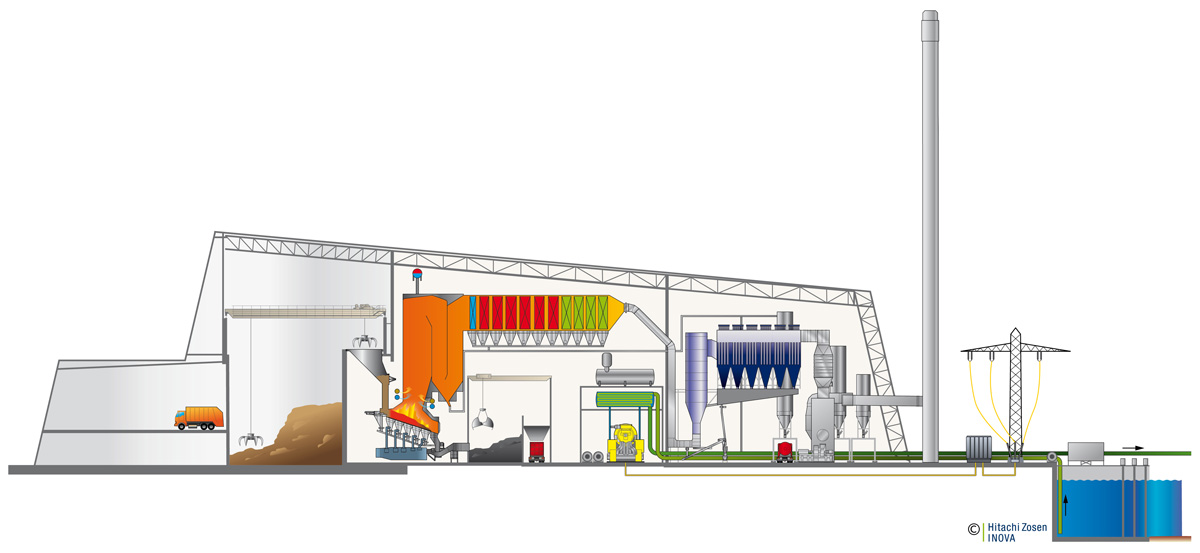
The WtE Process
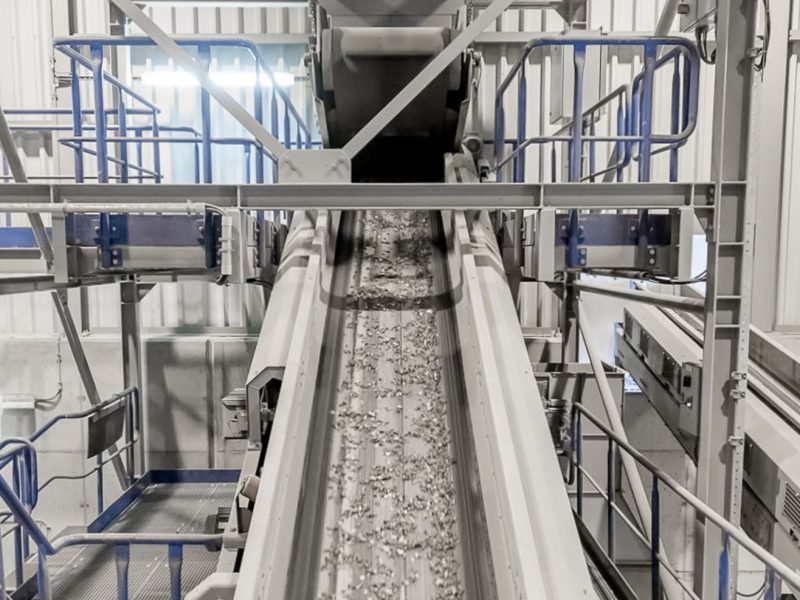
In a modern WtE plant, municipal solid waste is delivered to the site and stored in a bunker. A crane thoroughly mixes and feeds the waste into the feed hopper. From there it is pushed onto the grate by a ram feeder. A fully integrated control system ensures stable and efficient operation and optimises the fire position on the grate. Once combustion is complete, the inert ash that remains falls into the bottom ash extractor, from where it can be taken to a bunker or storage area for metals recovery and further use. The gases released from the waste are mixed with secondary air and recirculated flue gases above the grate. This assures complete combustion and the lowest CO, NOx and VOC emissions. Recirculation of flue gases also increases the plant’s energy efficiency. The energy released is used to produce superheated steam, which is expanded in a turbine generator to generate electricity. Flue gases are then cleaned to the strictest standards, and are continuously monitored before being released at the stack.








